HexSense
Fangzheng Liu, Nathan Perry, Ariel Ekblaw, and Joseph A Paradiso, 2025. "A Field Expedition and Parabolic Flight Experiment for the HexSense: A Type of Ballistic Deployed Self-Oriented Wireless Sensor Nodes for Future Lunar Exploration". In AIAA Scitech 2025 Forum. [PDF]
Fangzheng Liu, Cody Paige, Ariel Ekblaw, and Joseph A Paradiso. "HexSense: Self-Oriented Ballistic Deployed Wireless Sensor Nodes for Lunar Exploration". In Accelerating Space Commerce, Exploration, and New Discovery (ASCEND) 2024. [PDF]
Overview
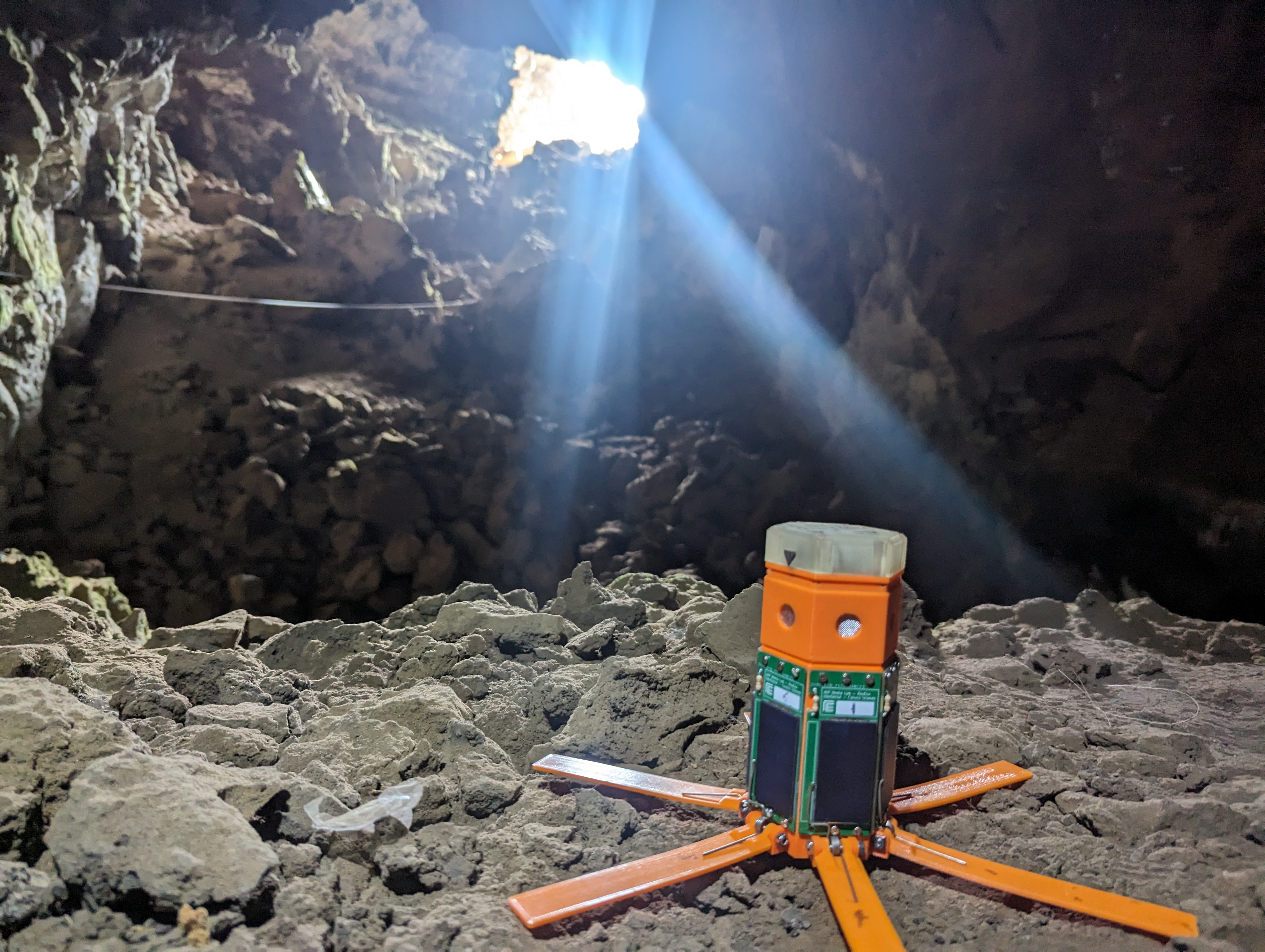
HexSense is a kind of Wireless Sensor node that can be ballistically deployed from rovers, and landers to the Lunar/Martian surface. After landing, the sensor node can automatically stand up and start collecting scientific data. Ballistically-deployed sensor nodes can extend the explorations of rovers and landers to hard-to-reach or dangerous areas (rock piles, steep crater rims, etc.) on the moon. Hardware redundancy can reduce the chance of failure and multiple sensor nodes can collect simultaneous data from multiple positions (compared with a rover, which can only take a series of single-point measurements), which is good for studying dynamic phenomena. Each sensor node is a modular design and can carry different sensor payloads based on data of interest, and here are three example sensor payloads.
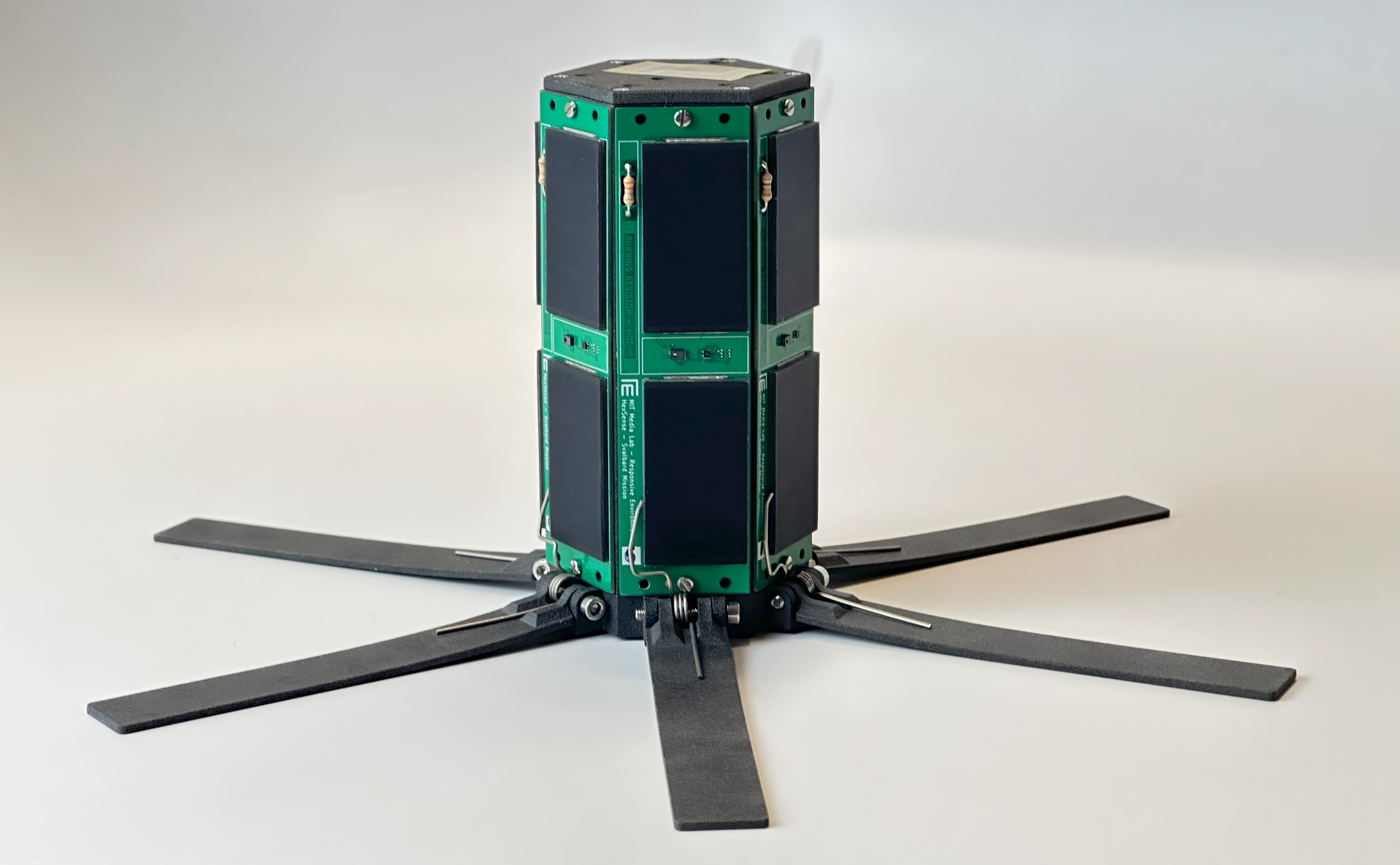
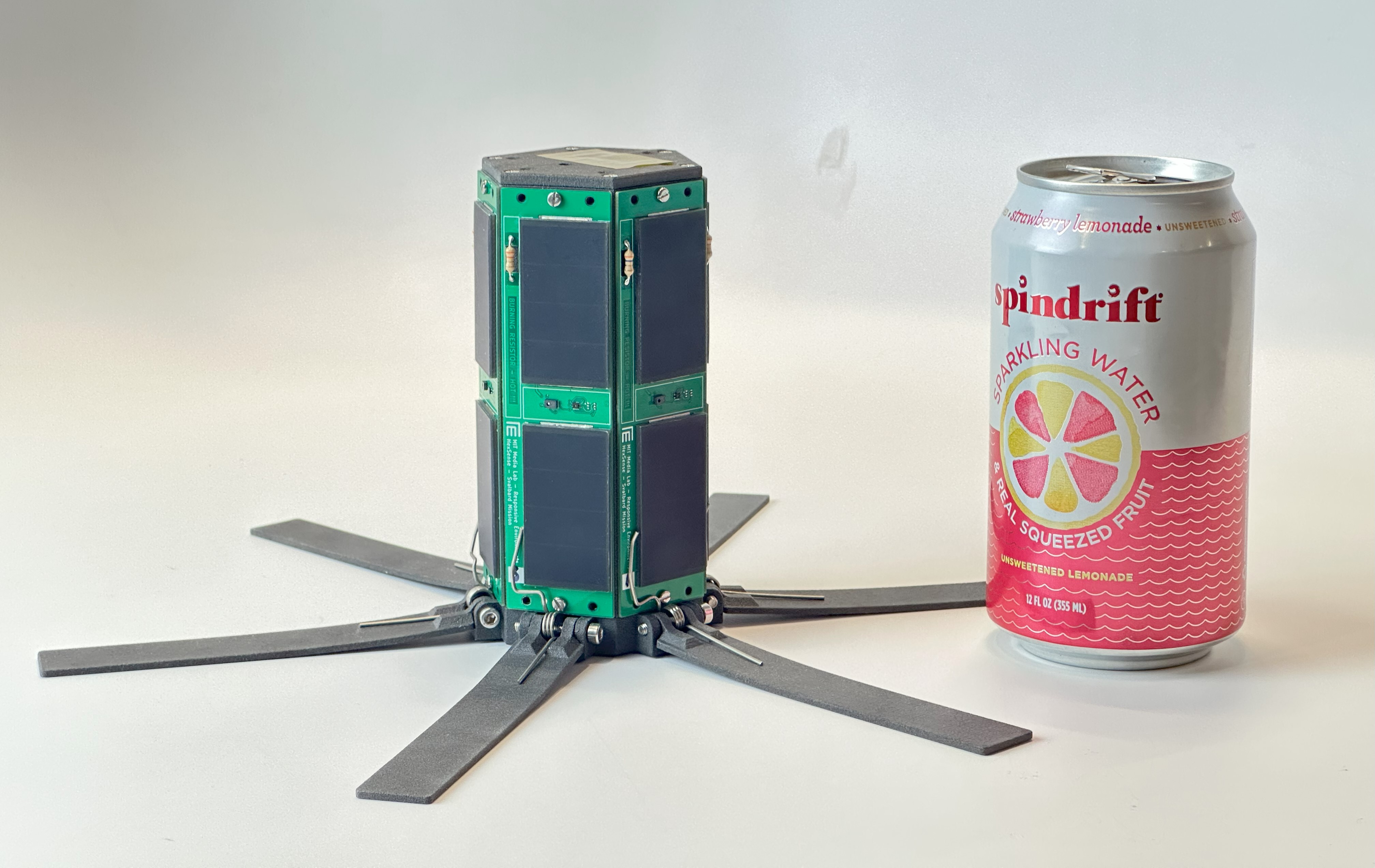
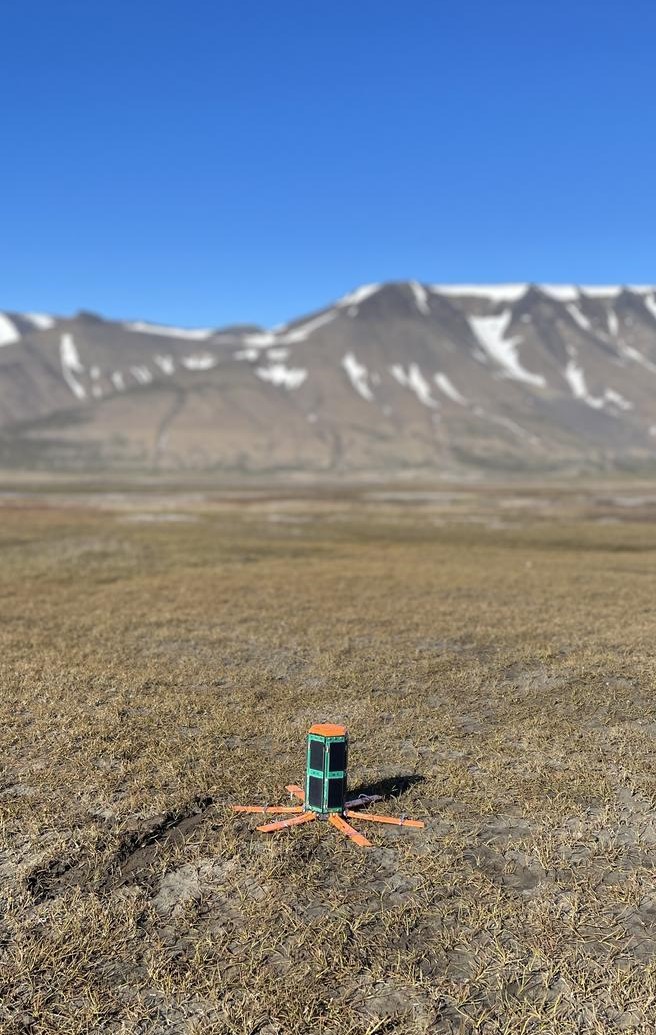
HexSense automatically standup after landed on the Lunar surface.
Design
The work is still in progress, and in the July of 2023, one HexSense node will be deployed to Svalbard in the Arctic area and collect environmental data for 10 days.


